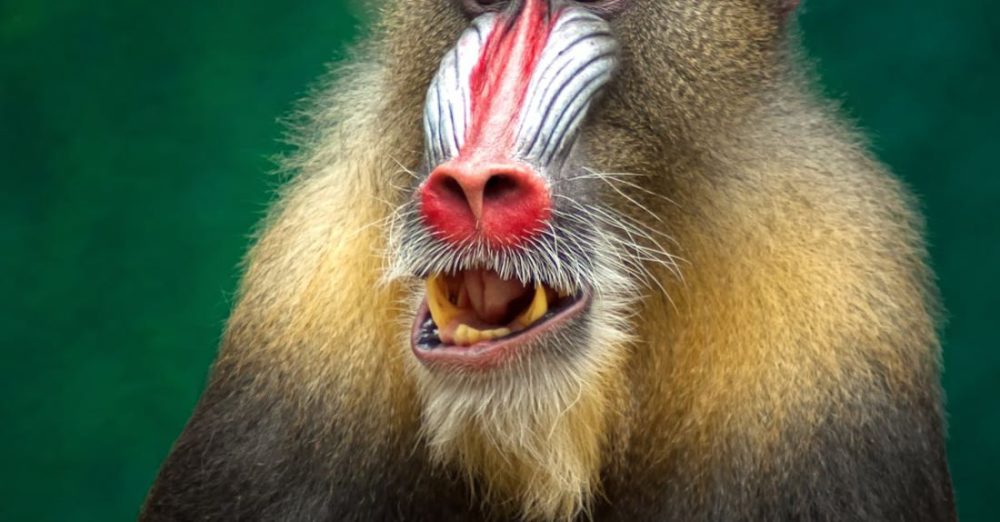
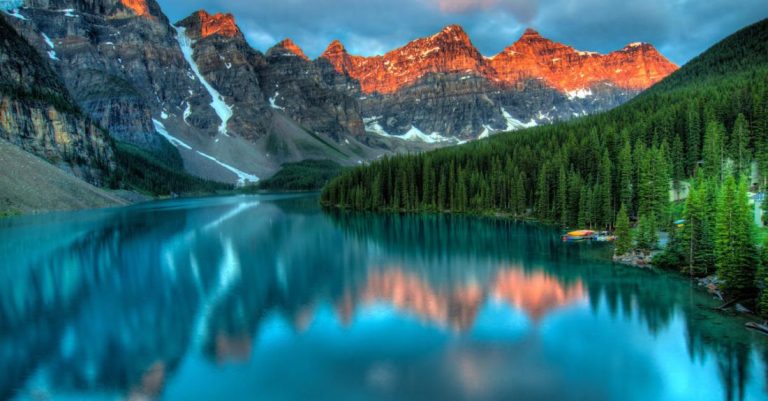
Protected areas play a crucial role in conserving biodiversity around the world. These designated regions, whether they are national parks, nature reserves, or marine sanctuaries, are established with the primary goal of safeguarding ecosystems, wildlife, and plant species from human activities that threaten their existence. The benefits of protected areas for biodiversity are numerous and essential for maintaining the delicate balance of our planet’s ecosystems.
Preserving Habitats
One of the key ways in which protected areas benefit biodiversity is by preserving habitats in their natural state. These areas provide a safe haven for a wide variety of species, allowing them to thrive without the pressures of habitat destruction, pollution, or human disturbance. By maintaining intact ecosystems, protected areas ensure that plants, animals, and microorganisms have the necessary conditions to survive and reproduce, contributing to the overall richness of biodiversity in these regions.
Biodiversity Hotspots
Protected areas often encompass regions that are considered biodiversity hotspots, which are areas with exceptionally high levels of species diversity and endemism. By conserving these hotspots, protected areas help safeguard unique and irreplaceable ecosystems that are home to a vast array of plant and animal species found nowhere else on Earth. Protecting these hotspots not only preserves the species living within them but also helps maintain the ecological processes and interactions that are essential for the functioning of these complex ecosystems.
Supporting Endangered Species
Many protected areas are established specifically to protect endangered species facing the threat of extinction. By providing a refuge for these species, protected areas give them a fighting chance to recover and increase their populations. The conservation efforts within these areas, such as habitat restoration, anti-poaching measures, and monitoring programs, play a crucial role in ensuring the survival of endangered species and preventing their disappearance from the wild. Through focused conservation actions, protected areas contribute significantly to the recovery of threatened species and the maintenance of overall biodiversity.
Connectivity and Migration Corridors
Protected areas also play a vital role in maintaining connectivity between different habitats and facilitating the movement of wildlife across landscapes. By creating corridors that link fragmented habitats, these areas allow species to migrate, disperse, and adapt to changing environmental conditions. This connectivity is essential for ensuring genetic diversity within populations, reducing the risk of inbreeding, and supporting the resilience of ecosystems in the face of climate change and other threats. Protected areas act as stepping stones that enable species to move freely and maintain healthy populations across their natural ranges.
Ecosystem Services and Human Well-being
In addition to their direct benefits for biodiversity, protected areas also provide essential ecosystem services that support human well-being. These services include clean water, air purification, carbon sequestration, soil fertility, and pollination, among others. By safeguarding these ecosystem functions, protected areas not only benefit wildlife and plants but also contribute to the health and sustainability of local communities that depend on these services for their survival. Recognizing the interconnectedness between biodiversity conservation and human well-being is crucial for ensuring the long-term success of protected areas in preserving ecosystems and species for future generations.
Sustainable Tourism and Education Opportunities
Protected areas also offer valuable opportunities for sustainable tourism and environmental education, raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity conservation and fostering a sense of stewardship among visitors. Ecotourism activities within protected areas can generate revenue that supports conservation efforts, local communities, and economies, while also promoting the appreciation and understanding of nature. Educational programs and interpretive materials in these areas help educate the public about the value of biodiversity, the threats it faces, and the actions needed to protect it. By engaging visitors in meaningful experiences and promoting responsible tourism practices, protected areas play a crucial role in advocating for biodiversity conservation on a global scale.
Preserving Biodiversity for Future Generations
In conclusion, protected areas are essential for safeguarding biodiversity and preserving the natural heritage of our planet for future generations. By protecting habitats, supporting endangered species, maintaining connectivity, providing ecosystem services, and promoting sustainable tourism and education, these areas play a critical role in conserving the wealth of life that sustains us all. It is imperative that we continue to expand and effectively manage protected areas to ensure the long-term survival of biodiversity and the countless benefits it provides to ecosystems and human societies alike. Only by working together to preserve these invaluable natural treasures can we secure a sustainable future for all life on Earth.